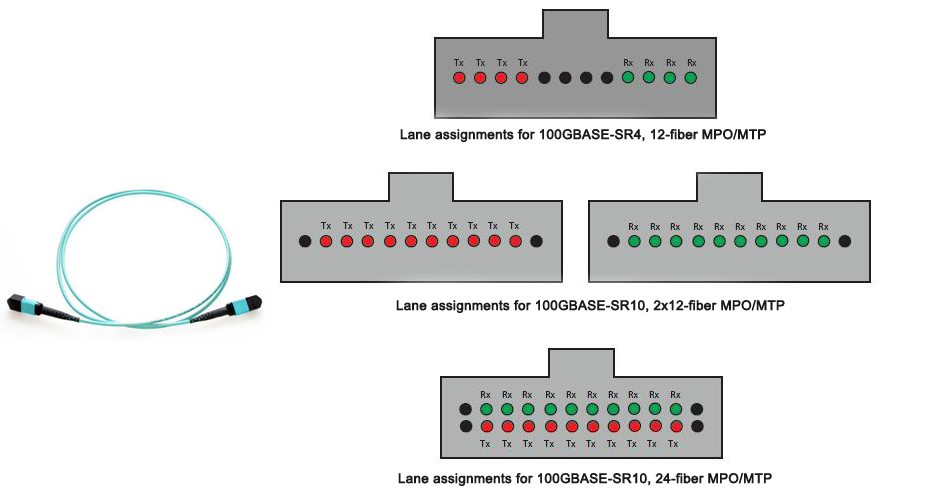
When talking about 40G cabling, MPO cable
is the most common choice for data center managers to use. Today, I’d
like to talk about three types of MTP cabling options for 40G parallel
connectivity. The first type is to deploy MPO 12 cable and ignore the
unused four fibers. And the other two types are using conversion module
or conversion harness to convert two 12-fiber links into three 8-fiber
links. So the three cabling options—no conversion vs. conversion module
vs. conversion harness: which to use for 40G parallel solution?
Solution 1: No Conversion
For
no conversion scenario, 12-fiber based MTP trunk cables are deployed in
the whole 40G connectivity. But in this situation, 33% fiber is not
used. And there will be additional cost associated with the purchase of
additional fiber. Moreover, the whole system includes unused fibers.
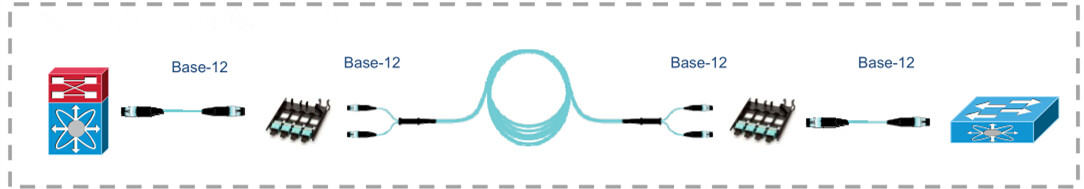
Figure 1: no conversion used, the whole link uses base-12 MTP/MPO cable
Solution 2: Conversion Module
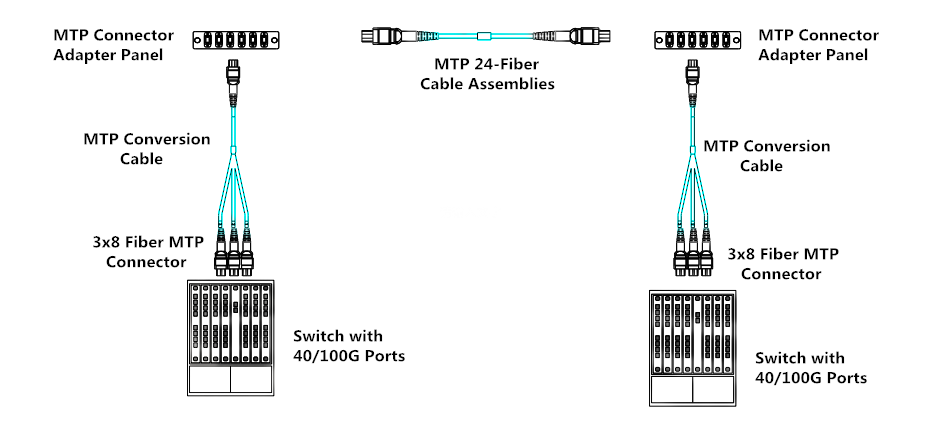
With
using conversion module, it can convert the unused fibers into usable
fiber links. For every two 12-fiber MTP connectors in the backbone
cable, you can create three 8-fiber links. Although there will be
additional cost for the additional MTP connectivity, it can be offset by
the cost savings from 100% fiber utilization in the structured cabling.
When reusing existing deployed MTP cabling, great value will be gained
if using conversion module to use all previously deployed fiber, and you
eliminate the cost of having to deploy additional cabling.
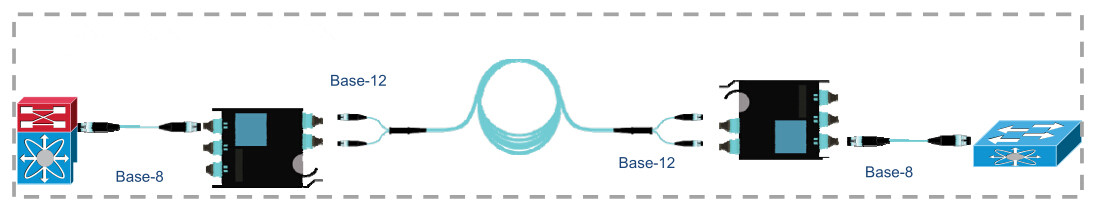
Figure 2: use conversion module to convert two 12-fiber links into three 8-fiber links
Solution 3: Conversion Harness
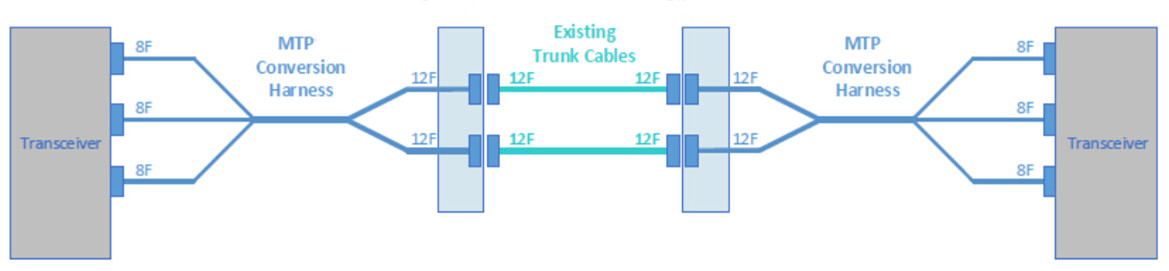
This
scenario uses standard MTP patch panels and 2x3 MTP conversion harness.
It does not add any connectivity to the link and full fiber utilization
is achieved. Although it seems attractive, it involves considerable
cabling challenges. For instance, if you only need two 40G connections
to the equipment, what do you do with the third 8-fiber MTP connection?
Or what if the 40G ports are in different chassis blades or completely
different chassis switches? The result will be long assemblies, which
will be difficult to manage in an organized way. For this reason, this
kind of solution is expected to be the least desirable and so the least
deployed method.
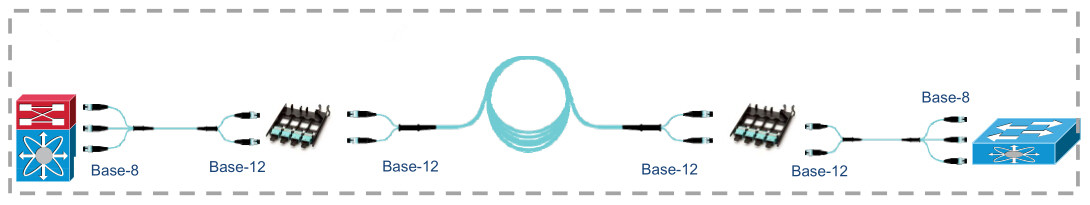
Figure 3: use conversion harness to convert two 12-fiber links into three 8-fiber links
No Conversion vs. Conversion Module vs. Conversion Harness
For
the three types of connectivity solutions, the “No Conversion”
solution, using traditional 12-fiber MTP connectivity and ignoring
unused fibers, has the advantage of simplicity and lowest link
attenuation. And as it does not use 33% of the installed fiber, it then
requires more cable raceway congestion.
The
“Conversion Module” solution, converting two 12-fiber links into three
8-fiber links through a conversion patch panel, uses all backbone fibers
and creates a clean, manageable patch panel with off-the-shelf
components. But it would lead to additional connectivity costs and
attenuation associated with the conversion device.
The
“Conversion Harness” solution, converting two 12-fiber links into three
8-fiber links through a conversion harness and standard MTP patch
panel, uses all backbone fibers with additional connectivity. But it
would create cabling challenges with dangling connectors and
non-optimized-length patch cords that require customization.
Generally,
the implementation of the conversion module solution is recommended,
especially if you are using previously installed MTP trunks. Conversion
module solution allows 100% fiber utilization while maintaining any port
to any port patching. And if you are installing new cabling, then you
can consider the no conversion solution, assuming that the cable raceway
is not a concern. The conversion harness solution is typically deployed
only in specific applications, such as at the ToR switch, where 40G
ports are in a close cluster and patching between blades in a chassis
switch is not required.
Conclusion
From
what have described above, have you had a better understanding of these
three types of 40G cabling solution? Each type has their own advantages
and disadvantages. For those three solution choices—no conversion vs.
conversion module vs. conversion harness: which is your choice for 40G
parallel solution?
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/no-conversion-vs-conversion-module-vs-conversion-harness.html