For
data center managers, deploying a fiber system that can easily be
upgraded to future high-density network demands is the first thing that
should be considered, because network reconfiguration would result in
lots of time and money. So it is essential to deploy a fiber network
which is easier to upgrade to the higher data rates from the start. For
high density MTP links, Base-8 vs. Base-12 vs. Base-24: which one can
provide a easier migration path for future network data rates?
Base-8 MTP Link
Base-8
MTP link is based on Type B male/pinned MTP trunk in the backbone.
Base-8 MTP is SR4 ready, meaning that the backbone connectivity has the
same fiber count as the SR4 transceiver. Base-8 MTP links allow
customers to patch directly to SR4 transceivers without having to
convert connectors with different fiber counts or waste excess fibers in
the backbone. As SR4 transceivers are the preferred choices for 40G,
100G data rates and beyond, the Base-8 system is arguably the most
scalable and future-proof backbone choice currently available. Customers
deploying 10G data rates today can still deploy the Base-8 system
knowing that upgrades to 40G or 100G will be much simpler and cost
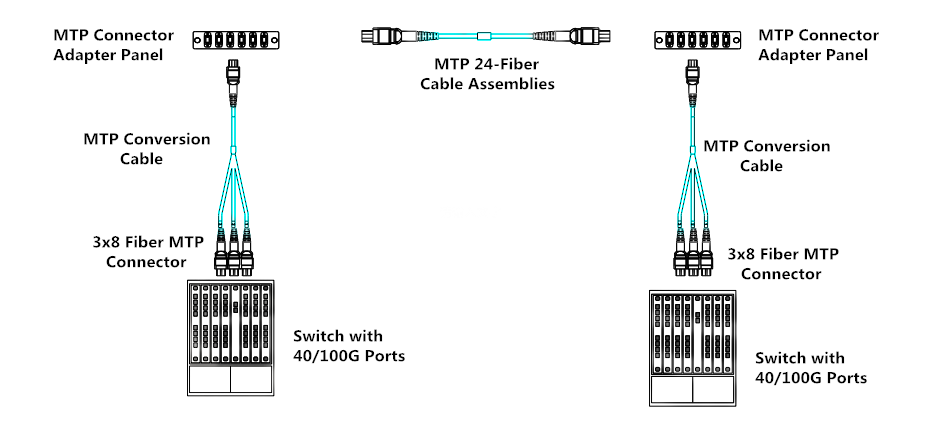
effective in the future. The following picture is 1x3 MTP conversion
harness cables used in 40G/100G network with 100% fiber utilization.
Base-12 MTP Link
Base-12
MTP link is based on Type A female/unpinned MTP trunk in the backbone.
Base-12 MTP is partially SR4 ready, because although SR4 is an 8 fiber
interface, the Base-12 MTP connector is still compatible with it. Unlike
the Base-8 MTP system, Base-12 does not utilize all of the fibers in
the backbone when patched directly with SR4 transceivers, however
multiple Base-12 MTP connectors can be combined and then converted so
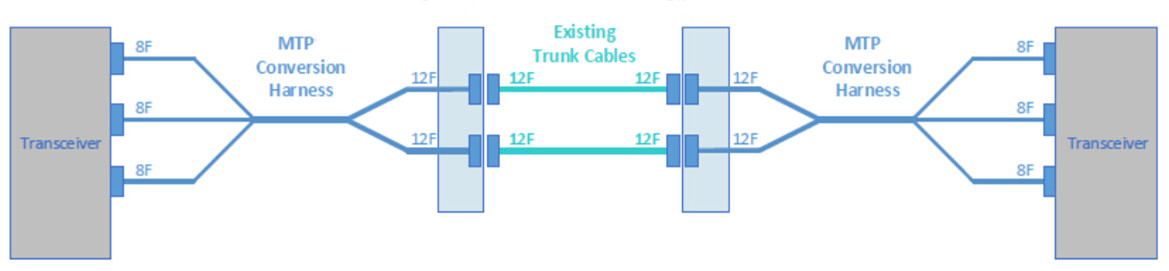
that full fiber utilization can still be achieved. Take our 2x3 MTP conversion harness
cables for example, these MTP conversion cables have two 12-fiber MTP
connectors on one end and three 8-fiber MTP connectors on the other end,
which utilize all 12 fibers in two trunks for use with three port
channels.
Base-24 MTP Link
Base-24
MTP link is generally deployed for 100G parallel links running over
SR10 transceivers. Normally these links are between two high data-rate
switches as opposed to switch to server. Base-24 can also be used for
lower data rate backbone links such as 10G and 40G but this is normally
only in cases where space and install time are the key drivers.
MTP Links: Base-8 vs. Base-12 vs. Base-24
- Initial Investment
Base-8
does require a higher up-front investment than Base-12 or Base-24
backbones due to the higher number of MTP connectors that are installed
from day 1. However, research shows that the rapid increase in data
rates will bring a return on investment within a few years. Furthermore,
Base-8 provides the most efficient link constructions for SR4 meaning
that the investment to convert Base-12 or Base-24 to SR4 will be largely
if not completely avoided later.
- Fiber Utilization
Although
Base-12 backbones are still the most common choice for most data center
operators today, it should be noted that there are still no
standardized transceivers using all 12 fibers in a Base-12 connector.
Furthermore, the most likely transceiver interface SR4 in the future
uses only 8 fibers. With this in mind, customers need to make the
important decision whether to deploy Base-12 today and risk wasting 33%
of backbone fibers tomorrow, or go straight for Base-8 knowing that it
will be the best investment for the future.
- No. of Cables
Compared
to Base-8 or Base-12, Base-24 reduces the number of cables required in
the link, and sometimes this can be a compelling driver towards using
this particular interface in the backbone. However, it should be noted
that deploying Base-24 as a backbone choice will require MTP transition
modules or MTP conversion harness to make it suitable for 10G and 40G
data rates.
Summary
From
what have described above, we can see that Base-8 MTP link, Base-12 MTP
link and Base-24 MTP link have their own cons and prons. Base-8 MTP
trunks allow users to build 10G links today but can easily be upgraded
to 40G links tomorrow using 8 fiber MTP connectivity. Base-12 and
Base-24 MTP trunks allow users to build 10G links today, which can
easily be upgraded to 40G/100G links tomorrow using MTP conversion
modules, MTP conversion harness or jumpers, but would result in 33%
fiber wastage. MTP Links: Base-8 vs. Base-12 vs. Base-24: which is your
choice?
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/mtp-links-base-8-vs-base-12-vs-base-24.html
Related Post: MTP-8 Solution: Future-Proof Connectivity in Data Center
没有评论:
发表评论