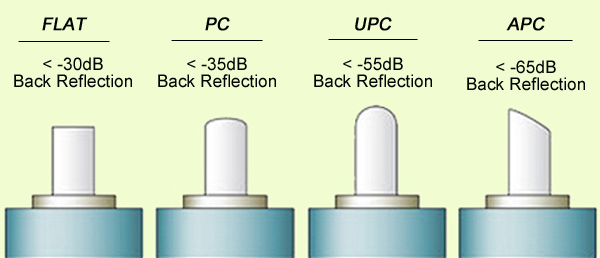
Growing
demand for high speed internet drives the new access technologies which
enable experiencing true broadband. This leads telecommunication
operators to seriously consider the high volume roll-out of optical
fiber based access networks. In order to allow faster connections, the
optical fiber gets closer and closer to the subscriber. Then FTTH (Fiber
To The Home) appears the most suitable choice for a long term objective
because it will be easier to increase the bandwidth in the future if
the clients are wholly served by optical fibers. FTTH is a future-proof
solution for providing broadband services.
Passive
optical network (PON) based FTTH access network is a
point-to-multipoint, fiber to the premises network architecture in which
unpowered optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber
to serve multiple premises, typically 32-128. The GPON FTTH access
network is highly emphasized in this article.
Components of GPON FTTH Access Network
Taking
advantages of WDM (wavelength division multiplexing), PON uses one
wavelength for downstream traffic and another for upstream traffic on a
single fiber. The OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is the main element of the
network. Placed in the Local Exchange, OLT is the engine that drives
FTTH system. OLT performs the function of traffic scheduling, buffer
control and bandwidth allocation. The optical splitter
splits the power of the signal and enables sharing of each fiber by
many users. ONT (Optical Network Terminal) is deployed at customer’s
premises and connected to the OLT through optical fiber and no active
elements are present in the link.
GPON FTTH Access Network Architecture
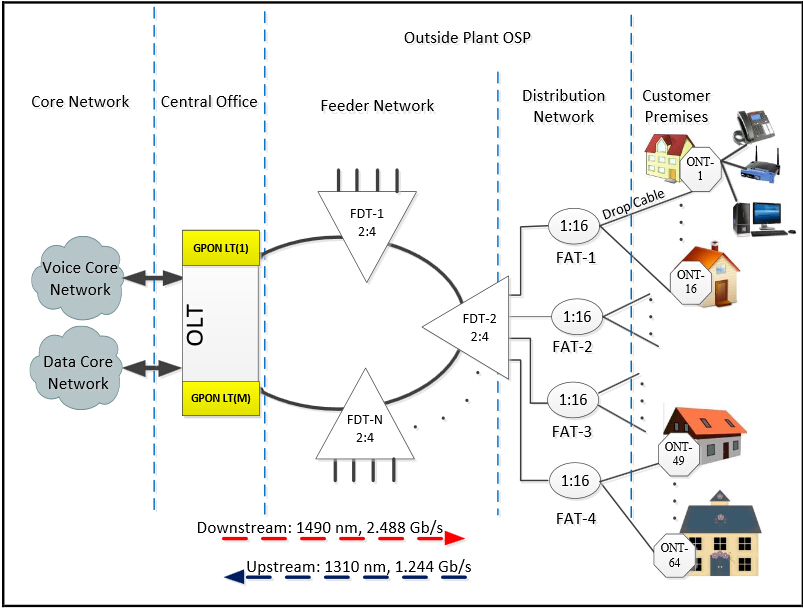
With
a tree topology, GPON is able to maximize the coverage with minimum
network splits, thus reducing optical power. A FTTH access network
comprises five areas, namely a core network area, a central office area,
a feeder area, a distribution area and a user area as shown in the
following diagram.
The
core network includes the ISP (internet service provider) equipment,
PSTN (packet switched or the legacy circuit switched) and cable TV
provider equipment. The main function of the central office is to host
the OLT
and ODF and provide the necessary powering. The feeder area extends
from ODF (optical distribution frames) in the CO (central office) to the
distribution points. Distribution cable connects level-1 splitter with
level-2 splitter. Level-2 splitter is usually hosted in a pole mounted
box placed at the entrance of the neighborhood. In the user area, drop
cables are used to connect the level-2 splitter to the subscriber
premises.
Traffic Flow in GPON FTTH Access Network
The
data is transmitted from OLT to ONT in downstream as a broadcast manner
and as a time division multiplexing (TDM) in upstream. The wavelength
of the downstream data is 1490 nm. Core network data services
transported over the optical network reaches the OLT and then
distributed to the ONTs through the FTTH network by dint of power
splitting. Every home receives the packets intended to it through its
ONT. The upstream represents the data transmission from the ONT to OLT
and the wavelength is 1310 nm. If the signals from different ONTs arrive
at the splitter input at the same time and at the wavelength 1310 nm,
it will lead to superposition of different ONT
signals when it reaches OLT. Thus TDMA is adopted to avoid the
interference of signals from ONTs. In TDMA time slots will be provided
to each user on demand for transmission of their packets. At the optical
splitter packets arrive in order and they are combined and transmitted
to OLT.
Conclusion
This
paper presents the components, architecture, and traffic flow in GPON
FTTH access network. The content may not be detailed, but GPON FTTH
network architecture is indeed reliable, scalable, and secure. It is a
passive network, so there are no active components from the CO to the
end user, which dramatically minimizes the network maintenance cost and
requirements. It is a future-proof architecture.
Article source: www.fiberopticshare.com/ftth-access-network-based-on-gpon-2.html