As
we all know, WDM (wavelength-division multiplexing) is a method of
multiplexing a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical
fiber by using different wavelengths (colors) of laser light. It enables
bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber, as well as
multiplication of capacity. In a WDM system, a multiplexer (Mux) is used
at the transmitter to join the several signals together, and a
demultiplexer (Demux) is used at the receiver to split the signals
apart. This article will focus on the CWDM & DWDM Mux/Demux.
CWDM Mux/Demux
CWDM
(coarse wavelength division multiplexing) is an excellent choice for
increasing bandwidth capacity while keeping costs down in short-range
communication networks. CWDM Mux/Demux modules are bidirectional passive
optical multiplexers and demultiplexers, allowing multiple optical
signals at different wavelengths to pass through a single optical fiber
strand. It can combine up to 18 different wavelength signals from
different optical fibers into a single optical fiber, or separates up to
18 different wavelength signals coming from a single optical fiber to
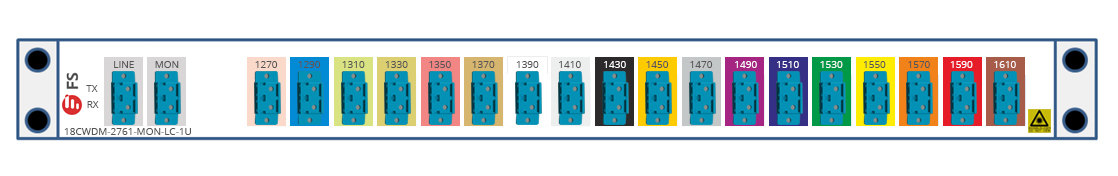
18 separate optical fibers. The following picture shows the front panel
of 18 channels 1270-1610nm dual fiber CWDM Mux Demux with monitor port.
DWDM Mux/Demux
DWDM
(dense wavelength division multiplexing) solution is the preferred
option for long-haul transmission. The DWDM Mux/Demux modules deliver
the benefits of DWDM technology in a fully passive solution. Usually,
they are used for long-distance transmission where wavelengths are
packed tightly together over the C-band range of wavelengths, up to 48
wavelengths in 100GHz grid (0.8nm) and 96 wavelengths in 50GHz grid
(0.4nm). Currently, the most common configuration of DWDM Mux/Demux is
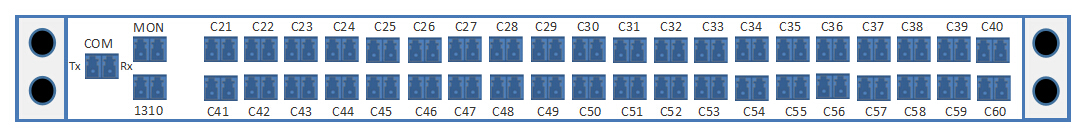
from 8 channels to 96 channels. The following picture shows the front
panel of 40 channels C21-C60 dual fiber DWDM Mux Demux with monitor port
and 1310nm port, which is ideally suited for high-density add/drop
requirements in DWDM networks.
Comparison Between CWDM and DWDM System
Price difference—CWDM
system carries less data, but the cabling used to run is less expensive
and less complex. A DWDM system has much denser cabling and can carry a
significantly larger amount of data, but it can be cost prohibitive,
especially where there is a need for a large amount of cabling in an
application.
Transmission distance—DWDM
system is designed for longer distance transmission as stated above.
They can transmit more data over a significantly larger run of cable
with less interference than a comparable CWDM system. If there is a need
for transmitting the data over a long range, DWDM system will likely be
the best in terms of functionality of the data transmittal and the
lessened interference over the longer distances that the wavelengths
must travel.
CWDM
system cannot transmit over long distances because the wavelengths are
not amplified, and therefore CWDM is limited in its functionality over
longer distances. Typically, CWDM can travel anywhere up to about 100
miles (160 km), while an amplified DWDM system can go much further as
the signal strength is boosted periodically throughout the run. As a
result of the additional cost required to provide signal amplification,
the CWDM solution is best for short runs that do not have mission
critical data.
FS.COM CWDM & DWDM Mux/Demux Solution
Multiplexing
enables a high density, scalable fiber solution. It allows an increase
in the fiber utilization by carrying multiple signals down an individual
fiber connection, rather than investing in more fibers. As a
professional manufacturer and supplier in telecommunication industry,
FS.COM offers a full range of CWDM & DWDM Mux/Demux. Our Mux/Demux
modules are designed for the best possible performance levels, which
helps to expand the bandwidth of optical communication networks with
lower loss and greater distance capacities. They are protocol
transparent and perfectly suit various applications, such as PDH,
SDH/SONET, Fibre Channel, etc. With different housing options, the end
users can easily add CWDM or DWDM capabilities to their existing or new
networks. For more details, please visit www.fs.com.
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/cwdm-dwdm-muxdemux-overview.html

