With
bandwidth demands continuing to grow, higher and higher capacity and
throughput are required in the data center. And to address these needs
efficiently and effectively, a strategic approach focusing on existing
user expectations and future capacity requirements is wanted. MTP/MPO
cable is the good choice that can meet various network requirements.
This post will list the roles of different MTP/MPO cables (MTP trunk,
MTP harness, MTP conversion harness) in 10G/40G/100G migration.
10G/40G/100G Migration Solutions
For
upgrading connection data rates, several common scenarios are available
with using MTP/MPO fiber cables. Following part will list these
applications out for your reference.
10G to 40G: 8-Fiber MTP Harness Cable
One
commonly used upgrade possibility beyond 10G incorporates four 10G SFP+
transceiver connections to a 40G QSFP+, which requires a 8-fiber MPO-LC
harness cable. Figure 1 illustrates one side of the transmission path
utilizing this MPO harness cable in conjunction with a 40G QSFP+ to
aggregate four 10G SFP+ transceivers. QSFP+ transceivers on the switches
yield higher port densities and throughput.
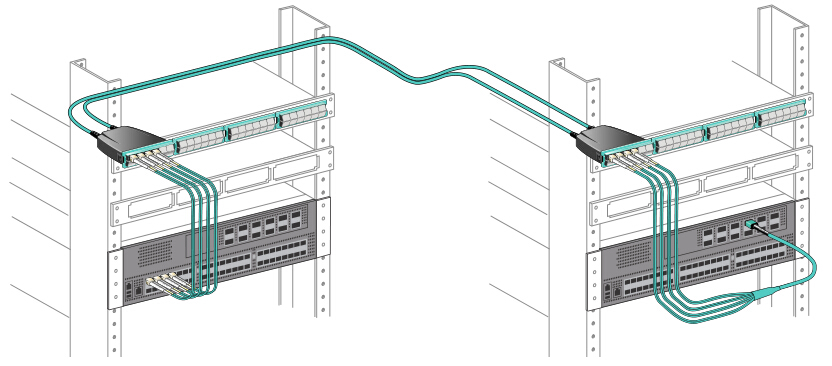
Figure 1: 10G to 40G upgrade by using MTP/MPO LC harness cable
40G to 40G: 12-Fiber MTP Trunk Cable
MTP trunk cable
incorporates interconnected banks of QSFP+ transceivers (MPO to MPO
connectivity). Figure 2 illustrates the connectivity. In this
connection, 12-fiber MPO trunk cables are needed to connect the
transceivers. Four fibers transmit light, four receive and four unused.
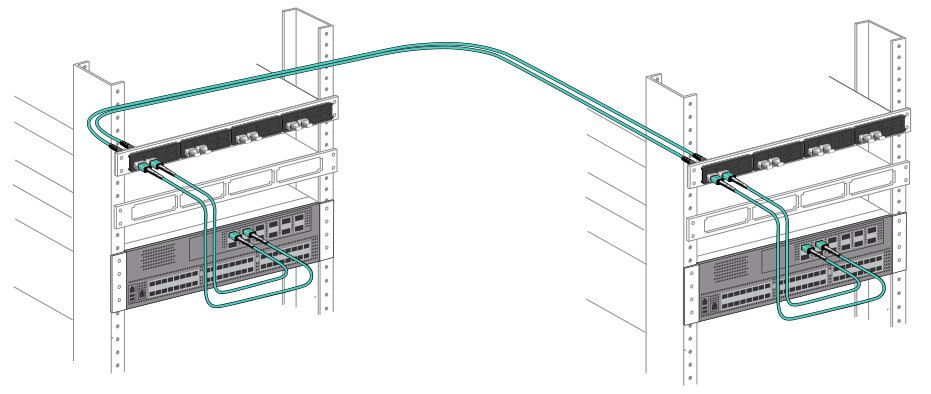
Figure 2: 40G to 40G connection by using MTP/MPO trunk cable with four fibers unused
40G to 40G: 2x3 MTP Conversion Harness/Module
MTP conversion harness
and MTP conversion module both take advantage of 100% fiber
utilization. For those needing 100% fiber utilization, 2x3 MTP
conversion harness or conversion module can achieve the purpose.
Connectivity of the 2x3 MTP conversion harness and conversion module is
the same. They are interchangeable, but must be used in pairs: one (MTP
conversion harness or module) at each end of the link. Figure 3 shows an
example of how MTP conversion module uses all fibers to achieve 100%
fiber utilization. The eight live fibers from each of the three QSFP+
transceivers are transmitted through the trunks using the full 24
fibers. The second 2x3 conversion module unpacks these fibers to connect
to the 3 QSFP+ transceivers on the other end.
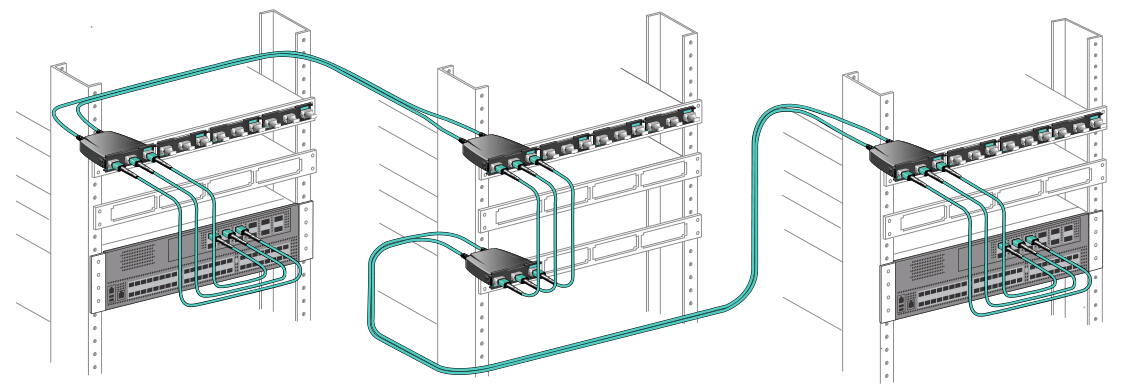
Figure 3: 40G to 40G connection with MTP conversion module ensuring 100% fiber utilization
100G to 100G: MTP Trunk Cable
For
100G to 100G connection, 24-fiber MTP trunk cable allows direct attach
capability of 100GBASE-SR10 CXP or CFP equipped devices, while 12-fiber
MTP trunk cable can be used to allow the direct connection for 100G
QSFP28 (MPO to MPO) connection.
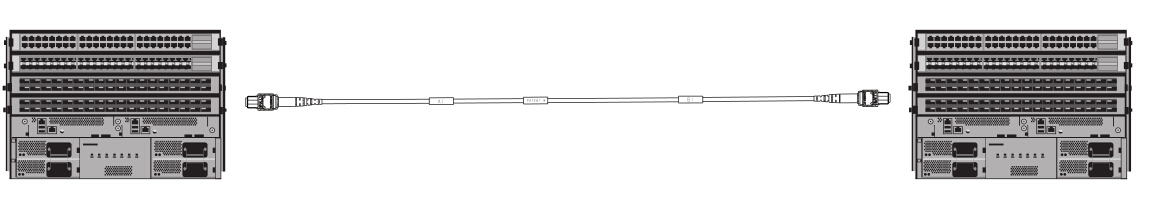
Figure 4: MTP trunk cable for 100G to 100G connection
10G to 100G/120G: 24-Fiber MTP Harness Cable
To
achieve 10G to 100G/120G connection, one popular implementation is to
use the high density 100G/120G CXP for space-saving. This deployment can
leverage the 10G-per-lane channels to distribute the 10G data anywhere
in the data center. Figure 5 uses a 24-fiber MTP harness cable
that separates each TX and RX pair, allowing connectivity to any duplex
path reachable by a patch panel. Simply connect this cable to a 120G
CXP transceiver and the customer can access the 12 individual
transceiver pairs. When used with a patch panel, this method offers the
ultimate in flexibility, allowing connectivity to any row, rack, or
shelf.
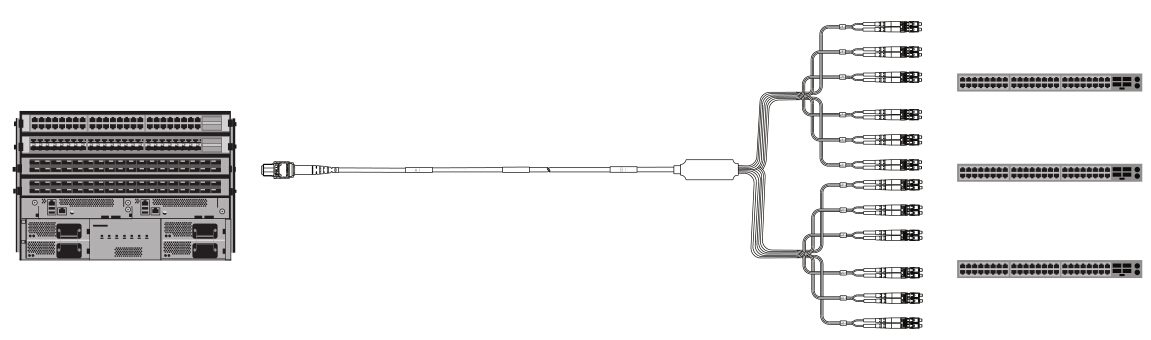
Figure 5: 10G to 100G connection by using 24-fiber MTP LC harness cable
40G to 120G: 1x3 MTP Conversion Harness
One
way to break out a 120G CXP is to use 1x3 MTP conversion harness cable.
Figure 6 shows a 24-fiber fanout that utilizes 24 fibers to split the
12 transceivers into three groups of eight. These eight-fiber groups
match the TX/RX fibers used on a QSFP+ transceiver for direct connection
to three separate QSFP+ transceivers. Like the 12x10G segregation
mentioned above, once split, the 3x8-fiber QSFP+ channels can be
distributed through patch panels and 12-fiber based trunking to any area
of the data center.
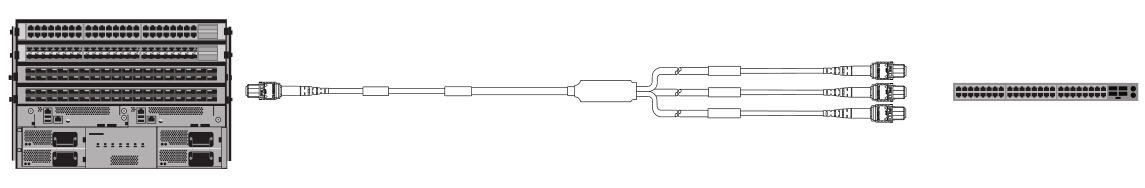
Figure 6: 40G to 120G connection by using 1x3 MTP conversion harness
Summary
Several
solution scenarios have been illustrated in this post. From 10G to
40G/100G/120G, we can see that different MTP/MPO fiber cables are used
for data transmission. Generally, MTP/MPO trunk cables are used for
direct connection between two switches. MTP harness cables are used for
data migration to higher data rates. And MTP/MPO conversion cables are
used to achieve 100% fiber utilization between two switches. All of
those different MTP/MPO fiber cables (MTP trunk, MTP harness, MTP
conversion harness) can be found in FS.COM. For more details, please
visit www.fs.com.
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/roles-mtp-trunk-mtp-harness-mtp-conversion-harness-40g100g-migration.html
没有评论:
发表评论