Pre-terminated
trunk cable assemblies provide an ideal plug-and-play solution for
links between switches, servers, patch panels, and zone distribution
areas in the data center. Compared with field-terminated cabling, the
pre-terminated cable assemblies can accelerate the process, reduce costs
and errors, and can help bring your data center online in less time.
This article will tell something about pre-terminated cabling.
What Can Pre-terminated Trunk Cables Achieve?
There are many benefits of deploying pre-terminated cable assemblies.
- Increase Speed of Deployment
Field
termination is the most time-consuming, labor-intensive part of the
cable installation process. Once pre-terminated cable assemblies are
delivered, they are ready for deployment, and can be connected quickly.
In many cases, pre-terminated cables can cut installation time by up to
80% over field terminations.
- No Need for Performance Testing
The
transmission testing of pre-terminated cable assemblies is performed by
the manufacturer before shipment, and test reports are included with
the assemblies. This leaves only continuity testing for copper and 10%
insertion loss and continuity testing for fiber, which reduces the time
spent testing on-site.
- Reduce Downtime With Faster, More Flexible MACs
With
pre-terminated solutions, data center managers can make changes quickly
based on network growth, business decisions, or shifting requirements.
In disaster recovery situations that call for fast, temporary data
communications set-up, pre-terminated cabling can minimize business
downtime and establish communications quickly. It can be disassembled
quickly when the situation is resolved. The components are reusable for
more efficient moves, adds, and changes (MACs).
- Cut Clean-up Time
Pre-terminated
solutions allow for quick clean-up due to minimal leftover materials
and scrap. Also, because there is less waste material to clean up,
pre-terminated solutions also help meet green design, waste reduction,
and material reuse goals.
Common Types of Pre-terminated Trunk Cables
There
are pre-terminated fiber cabling and pre-terminated copper cabling.
This part will introduce two kinds of commonly used pre-terminated trunk
cable assemblies: pre-terminated fiber trunk cable, and pre-terminated
copper trunk cable.
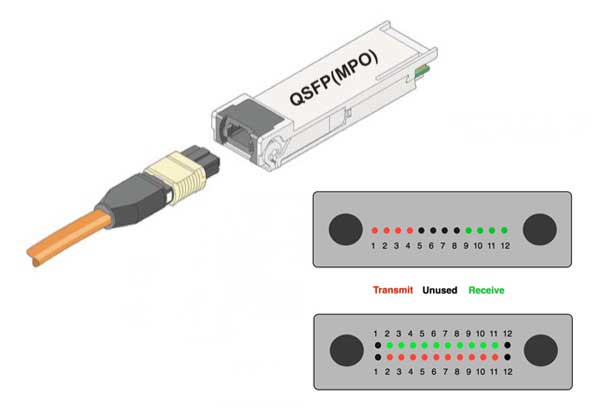
- MTP/MPO Trunk Cables
Pre-terminated
with MTP/MPO connectors on both ends, the MTP/MPO trunk cables provide a
quick-to-deploy, scalable solution that improves reliability and
reduces installation time and cost. They are capable of supporting
multiple users or devices from one point to another while distributing
multiple data channels, which is a convenient and economical alternative
to running multiple jumpers or patch cables. Generally 12-fiber MTP/MPO
trunk cables and 24-fiber MTP/MPO trunk cables are commonly used
separately for 40G applications and 100G applications. The following
picture is a 12-fiber female to female MTP single-mode trunk cable.

There
are also high fiber count MTP/MPO trunk cables which have several legs
on both ends. The following picture shows a 72-fiber MTP/MPO trunk
cable. There are 6 legs on both ends with each leg terminated with a
12-fiber MTP/MPO connectors.

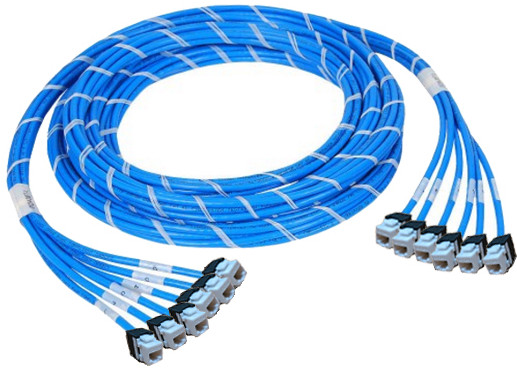
- Pre-terminated Copper Trunk Cables
The
pre-terminated copper trunk cable is a bundle of category cables, built
with a choice of 6, 12, or 24 cable bundle and factory terminated with
jacks and plugs. They allow fast and easy installation with reduced
labor costs in large copper infrastructures with high-density
cross-connection and patching systems. The pre-terminated copper cable
assemblies offered by FS.COM are pre-bundled and pre-labeled styles,
available in Cat 5e, Cat 6 and Cat 6a UTP and STP cable constructions
with each available in jack to jack, plug to plug and jack to plug
termination ends.
How to Choose the Suitable Pre-terminated Trunk Cables?
When selecting pre-terminated cable assemblies, the following tips are for your reference.
- Be sure to use a reliable vendor that can offer services such as guaranteed cabling performance, design assistance, certified contractor training, and the ability to support large quantities of assemblies in the required delivery window.
- Make sure the pre-terminated fiber or copper cabling purchased through a manufacturer uses components that have been tested and verified by a third party to exceed TIA and IEEE standards. The manufacturer should also provide 100% testing in a quality-controlled environment before the cabling is shipped out to the work site.
Summary
Pre-terminated
trunk cable assemblies are perfect for data centers and other
applications where speed and testing simplify installation. They help to
save time, and labor. FS.COM provides various kinds of high-quality but
low-price pre-terminated cable assemblies. And all of them are tested
before shipment. If you need, please visit www.fs.com.
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/basis-pre-terminated-trunk-cable-assemblies.html