Nowadays,
fiber optic network is gaining its popularity because it has high
speed, high density and high bandwidth, etc. Compared with traditional
copper cable, the fiber optic cable could support much further distance
although the exact distance is limited by many factors. For the super
fast optical communication, transmission distance has already become the
most vital issue. The optical signal may become weak over long
distance. Thus, many components and methods have been adopted to break
the limitations of the optical transmission distance. This article will
emphasize the factors that limit optical transmission distance.
Optical Fiber Cable Type
Typically,
the dispersion in the fiber optic cable could have a great impact on
the transmission distance. There are two types of dispersion—chromatic
dispersion and modal dispersion. Chromatic dispersion is the spreading
of the signal over time resulting from the different speeds of light
rays, while modal dispersion is the spreading of the signal over time
resulting from the different propagation mode.
As it is known to all, optical fiber cable could be divided into single-mode fiber cable
and multimode fiber cable. For the single-mode fibers, transmission
distance is affected by chromatic dispersion, because the core of
single-mode fibers is much smaller than that of multimode fibers. And
this is the main reason why single-mode fiber can have longer
transmission distance than multimode fiber. For the multimode fibers,
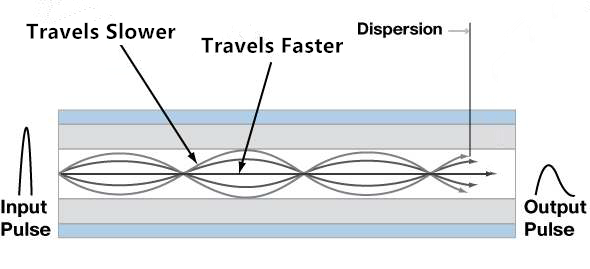
transmission distance is largely affected by the modal dispersion. Due
to the fiber imperfections, the optical signals of multimode fibers
cannot arrive simultaneously and there is a delay between the fastest
and the slowest modes, which causes the dispersion and limits the
performance of multimode fibers (see the following picture).
Light Source of Fiber Optic Transceiver
Fiber
optic cable is the path sending the optical signals. However, most of
the terminals are electronic based. The conversions between electrical
signals and optical signals are necessary. Fiber optic transceivers
are widely used in today’s optical network to achieve this purpose. The
conversion of signals depends on a LED (light emitting diode) or a
laser diode inside the transceiver, which is the light source of fiber
optic transceiver. The light source can also affect the transmission
distance of a fiber optic link.
LED
diode based transceivers can only support short distances and low data
rate transmission. Thus, they cannot satisfy the increasing demand for
higher data rate and longer transmission distance. For longer and higher
transmission data rate, laser diode is used in most of the modern
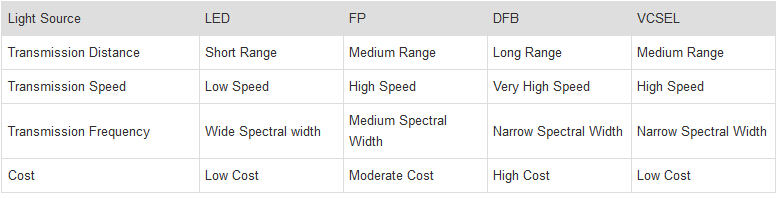
transceivers. The most commonly used laser sources in transceivers are
Fabry Perot (FP) laser, Distributed Feedback (DFB) laser and
Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting (VCSEL) laser. The following chart
shows the main characteristics of these light sources.
Frequency of Transmission
As
is shown in the above chart, different laser sources support different
frequencies. The maximum distance of fiber optic transmission system can
support is affected by the frequency at which the fiber optic signal
will be transmitted. Generally the higher the frequency, the longer
distance the optical system can support. So it is essential to select
the right frequency to transmit optical signals. Typically single-mode
fibers use frequencies of 1300 nm and 1550 nm, while multimode fibers
use frequencies of 850 nm and 1300 nm.
Bandwidth
Another
factor influencing the transmission distance is the bandwidth of fiber
optic cables. Generally, the transmission distance decreases
proportionally, as the bandwidth increases. For example, a fiber that
can support 500 MHz bandwidth at a distance of one kilometer will only
be able to support 250 MHz at 2 kilometers and 100 MHz at 5 kilometers.
Single-mode fibers have an inherently higher bandwidth than multimode
fibers due to the way in which light passes through them.
Splices and Connectors
Splices
and connectors in most fiber optic system are inevitable. Signal loss
can be caused when the optical signal passes through each splice and
connector. The total amount of the loss depends on the types, quality
and number of connectors and splices.
Conclusion
According
to the above statement, the optical transmission distance is affected
by various factors including the fiber type, light source of
transceiver, frequency of transmission, bandwidth as well as splices and
connectors. So it is necessary to consider these factors to minimum the
limitations on transmission distance when deploying the fiber optic
network.
Article source: www.roarsummit.com/factors-that-limit-optical-transmission-distance-1562133546.html
没有评论:
发表评论