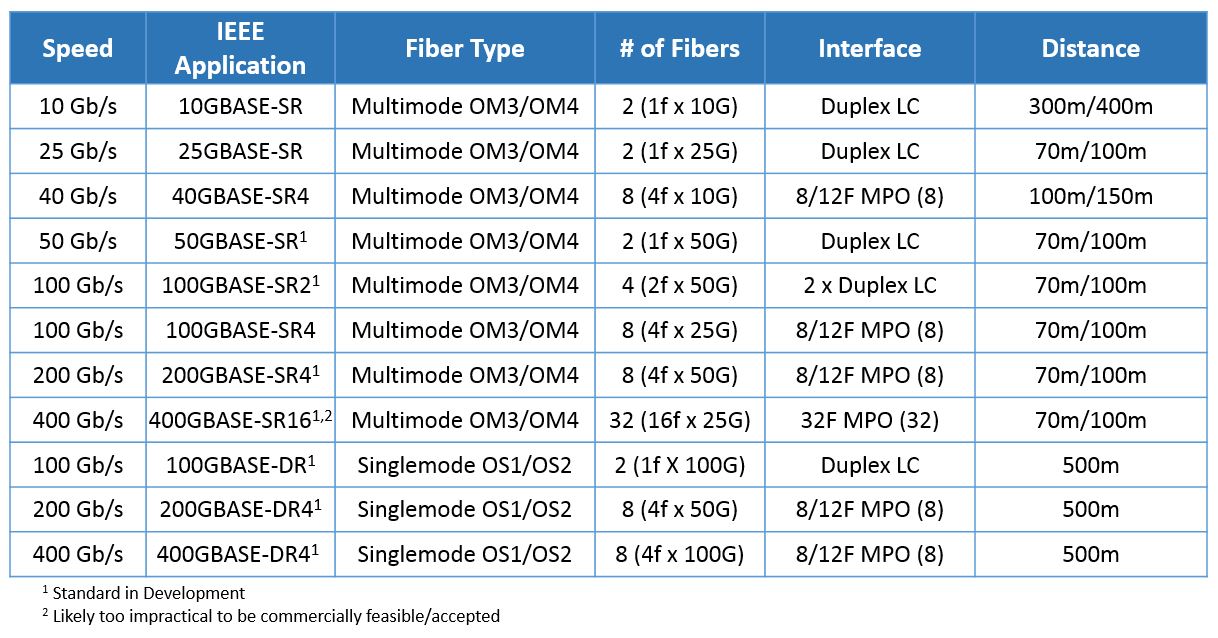
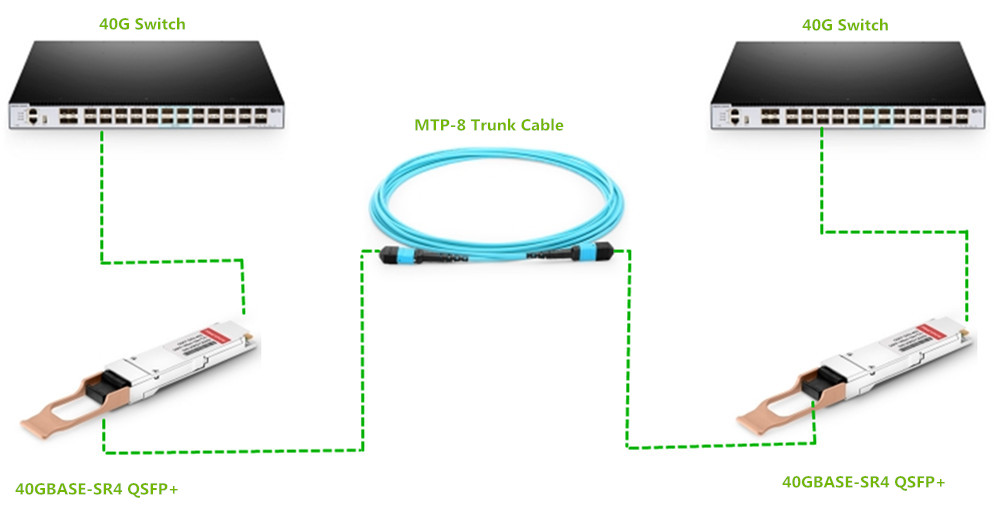
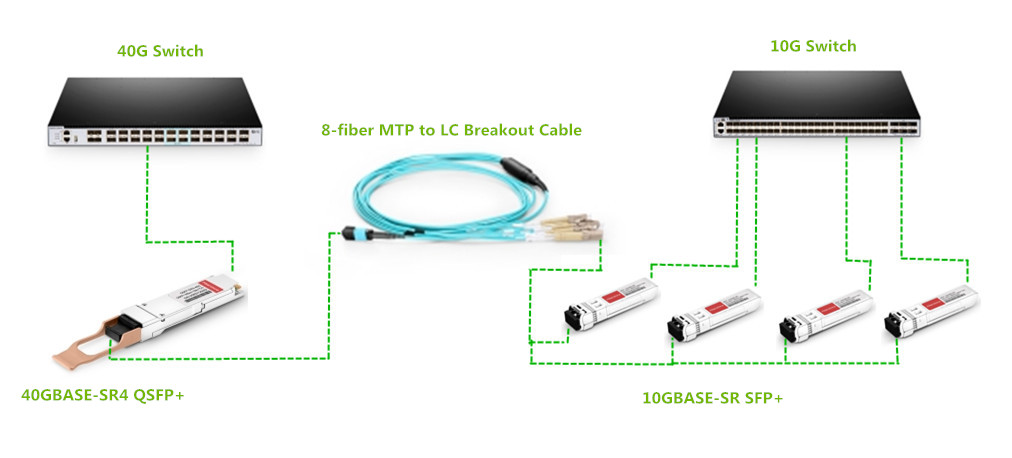
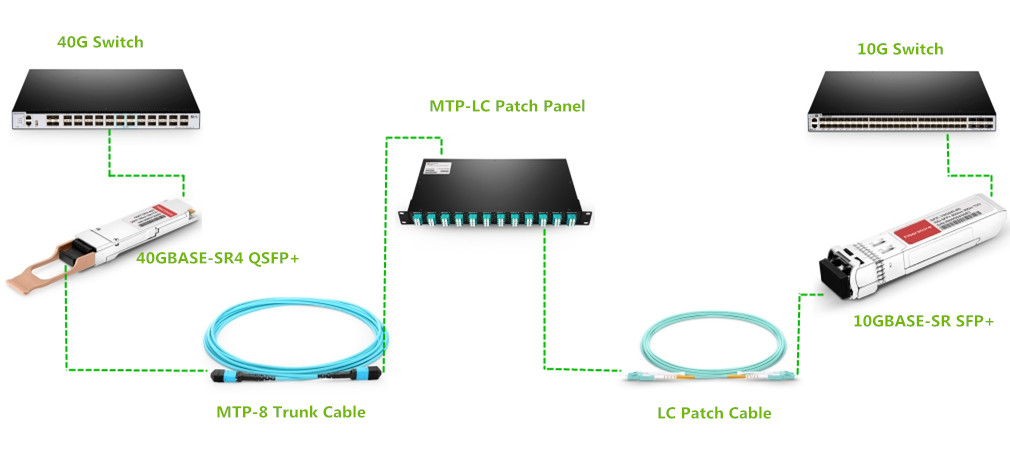
In the previous post—Modular Patching Solutions for Flexible Cable Management,
I have introduced one kind of FHD fiber enclosure with user-friendly
slide-out drawer and flexible mounting options. Actually, besides that
rack mount fiber enclosure, there is another kind of FHD fiber enclosure
useful in cable running and managing: wall mount fiber enclosure. It is
very convenient for multi-floor cabling. This post will tell how to run
cables in multi-floor data center by flexible usage of fiber
enclosures.
Fiber Enclosure – One Key Component for Cable Routing and Managing
Both
wall mount fiber enclosure and rack mount fiber enclosure can be used
in the multi-floor data center. Here I only say something about wall
mount fiber enclosure as rack mount ones have been introduced in the
previous post.

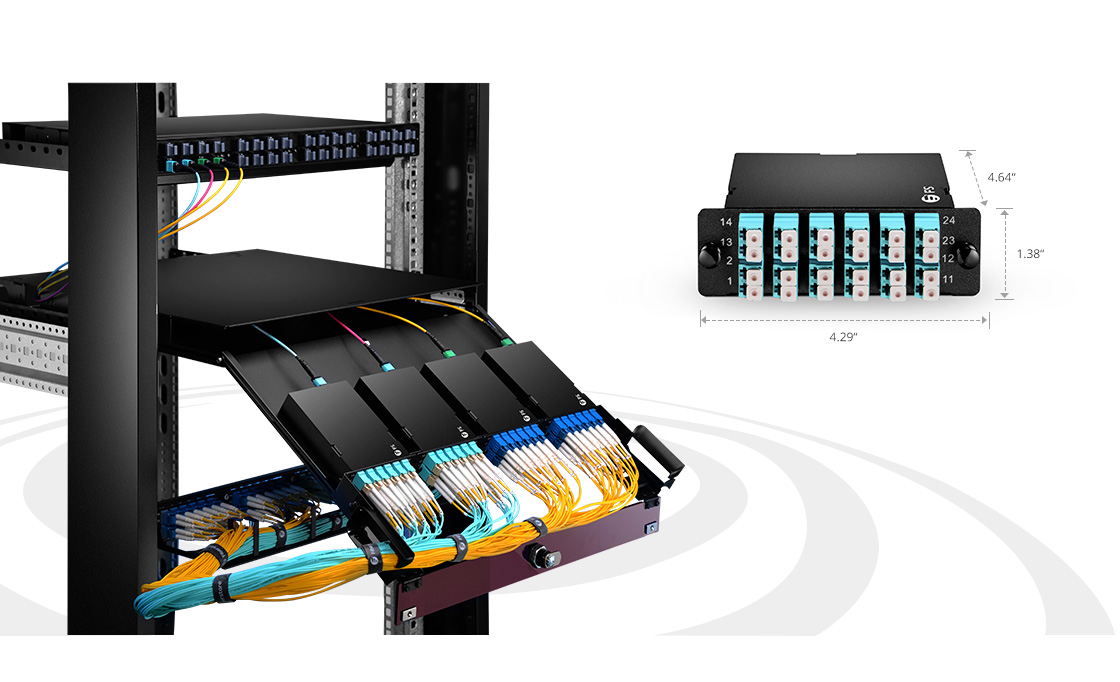
Figure 1: Wall mount fiber enclosures with two mounting options
As
the name shows, wall mount fiber enclosures are usually installed on
the wall for cable routing and managing. Take FS.COM wall mount fiber
enclosure for example, the wall mount fiber enclosures can be loaded
with 2, 4, 8 fiber adapter panels and 2 slack spools for easy-to-manage
environment for fiber patch cables, or 2, 4, 8 MTP cassettes for maximum
density in limited spaces while reducing installation time.
User Case Scenario Analysis
Usually
there are racks and racks or cabinets and cabinets in the data center.
Proper cable connecting among the racks is vital to future cable moves,
adds and changes. Generally, fiber enclosures are a good way and used to
route and manage fiber cables. This part will show one user case
scenario to tell how to run cables in multi-floor data center. The
following picture demonstrates the situation.
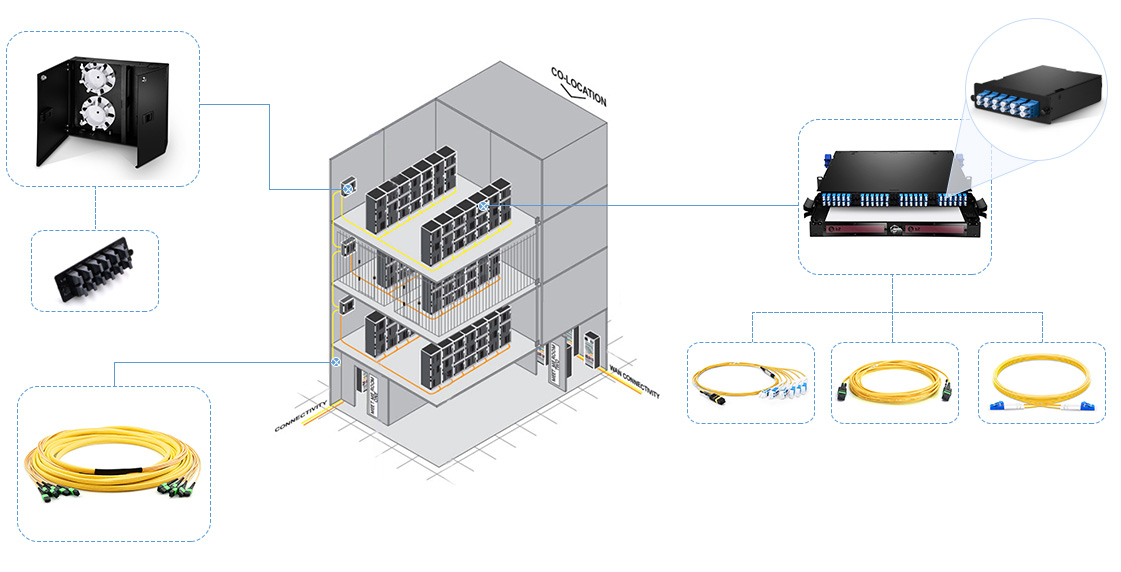
Figure 2: Multi-floor data center cable routing scenario
In
this case, the wall mount fiber enclosures loaded with MTP fiber
adapter panel and the rack mount fiber enclosure loaded with MTP
cassette are used to manage the fiber cables. The MPO fiber cables
can be used to provide backbone interconnection between data center
distribution zone areas and provide patching for parallel transceiver or
array equipment. There are standard 12f and 24f MPO trunk cables as
well as 48f MPO trunk cable and 72f MPO trunk cable. MTP cassettes
installed inside the fiber enclosure can be used to connect the front LC
fiber jumpers to the back MPO fiber cables. Or the MTP cassettes can be
replaced with MTP fiber adapter panel for direct trunk cable to fan out
interface. No matter how you run your data center cabling, fiber
enclosures are undoubtedly important for routing and managing the fiber
cables with flexible MACs—wall mount fiber enclosure for cable
connecting between floor and floor while rack mount fiber enclosure for
cabling connecting between or within racks and racks.
What Can We Summarize?
Using MTP/MPO cassettes, MPO fiber cables, and fiber enclosures
are smart way to deploy your network neatly, conveniently and flexibly.
They can build a complete easy-to-manage system in the multi-floor data
center. Deploying the fiber enclosures and MPO fiber cables at first
for good management will do better than re-routing and re-configuring
the cabling at last. Do you think so? If “Yes”, buy the MTP cassettes,
fiber enclosures and MPO fiber cables from FS.COM with the most
competitive price! More details, visit www.fs.com.
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/run-cables-multi-floor-data-center-fiber-enclosures.html