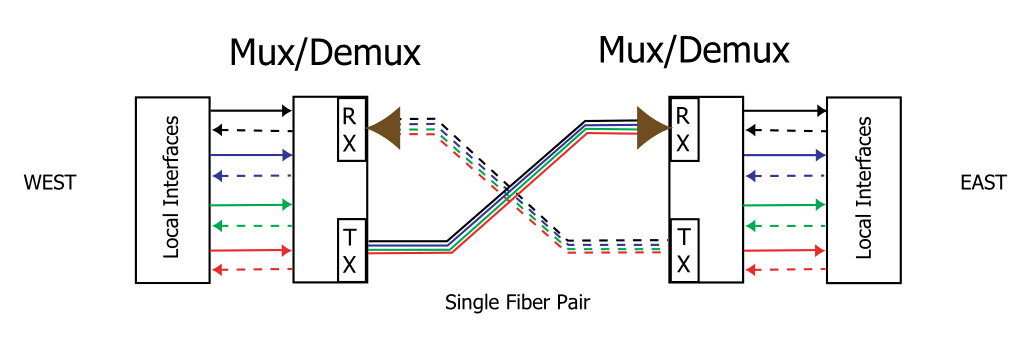
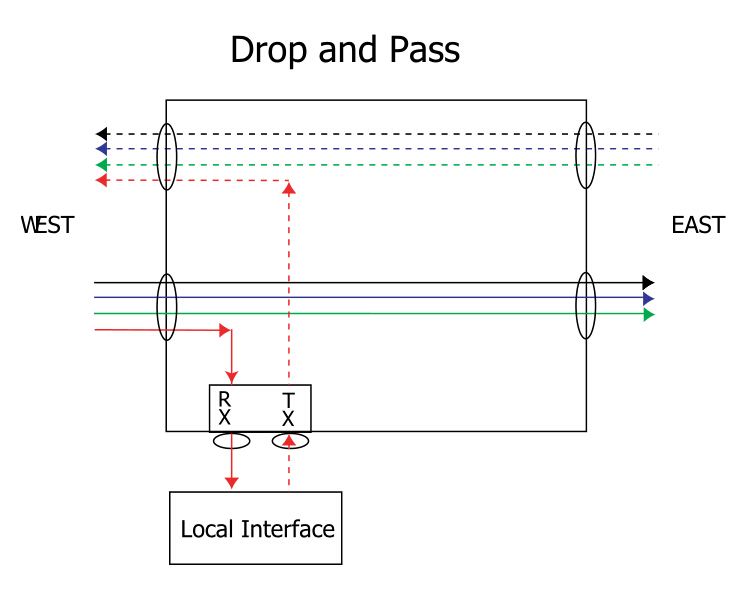
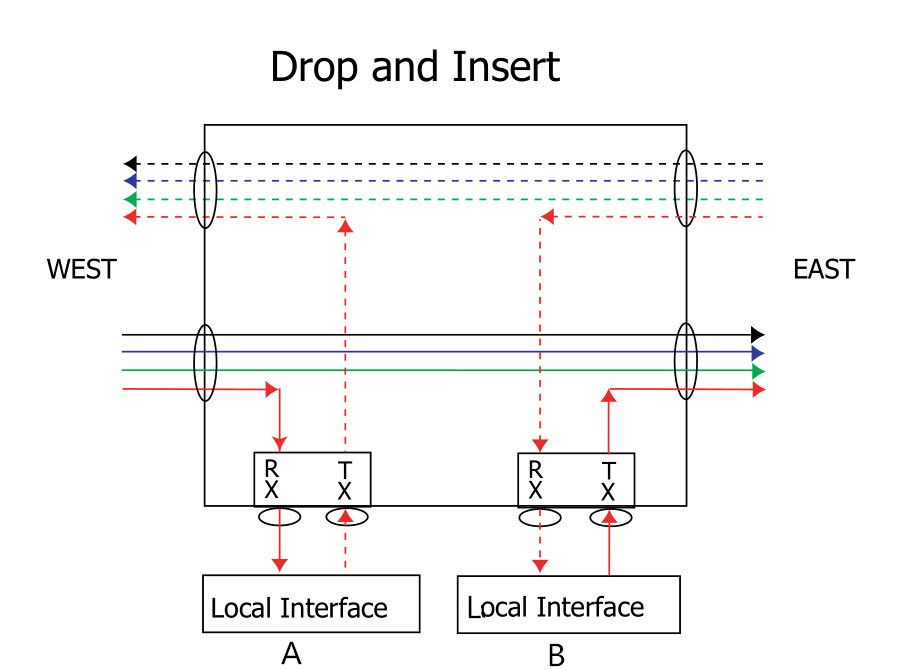
CWDM
system is able to provide optical networking support for high-speed
data communication for metropolitan area networks (MANs). And in some
previous articles, I have talked a lot about CWDM, such as the components used in CWDM system. In this article, I’d like to have an introduction to CWDM system installation and connection.
Procedures for CWDM System Installation
The
CWDM system includes the system shelf, CWDM OADM, CWDM Mux/Demux and
CWDM transceivers. You must first install the system shelf, then the
CWDM OADM and CWDM Mux/Demux, followed by the CWDM transceivers you want
to install.
Install the System Shelf
Follow the steps below to mount the system shelf on an equipment rack:
1. Align the mounting holes in the L brackets with the mounting holes in the equipment rack.
2.Secure
the system shelf using four screws through the elongated holes in the L
bracket and into the threaded holes in the mounting post.
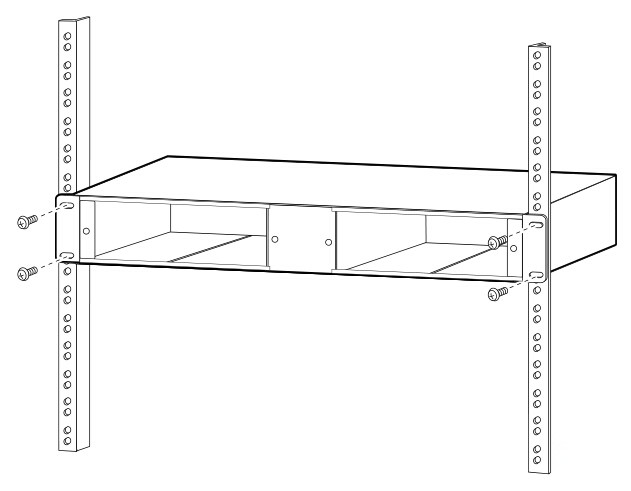
3.Use a tape measure and level to ensure that the system shelf is mounted straight and level.
Install the CWDM OADM and CWDM Mux/Demux (Plug-in Module)
1.Loosen the captive screws on the blank plug-in module faceplate and remove the faceplate.
2.Align the plug-in module with the slot on the system shelf.
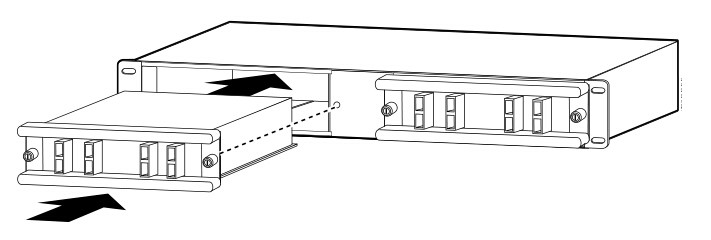
3.Gently
push the plug-in module into the system shelf slot. Ensure that you
line up the captive screws on the plug-in module with the screw holes on
the shelf.
4.Tighten the captive screws.
Remove the CWDM OADM and CWDM Mux/Demux (Plug-in Module)
1.Loosen the captive screws on each side of the plug-in module using a screwdriver.
2.Gently pull on both captive screws to release the plug-in module from the shelf.
3.Pull the plug-in module out of the shelf.
4.Replace the blank plug-in module faceplate if you do not intend to install another plug-in module.
Install a CWDM Transceiver
1.Remove the CWDM transceiver from its protective packaging.
2.Verify that the CWDM transceiver is the correct model for your network configuration.
3.Remove the dust covers from the CWDM transceiver’s optical bores.
4.Grasp the sides of the CWDM transceiver with your thumb and forefinger.
5.Insert
the CWDM transceiver into the correct slot on your switching module.
You should hear a click when the transceiver has been properly seated
into the slot.
Remove a CWDM Transceiver
1.Disconnect the fiber optic patch cable.
2.Release the CWDM transceiver from the slot by simultaneously squeezing the plastic tabs.
3.Pull the CWDM transceiver out of the slot.
4.Install the plug in the CWDM transceiver optical bores and place the CWDM transceiver in protective packaging.
Procedures for CWDM System Connection
This part tells how to connect the CWDM system to the switch.
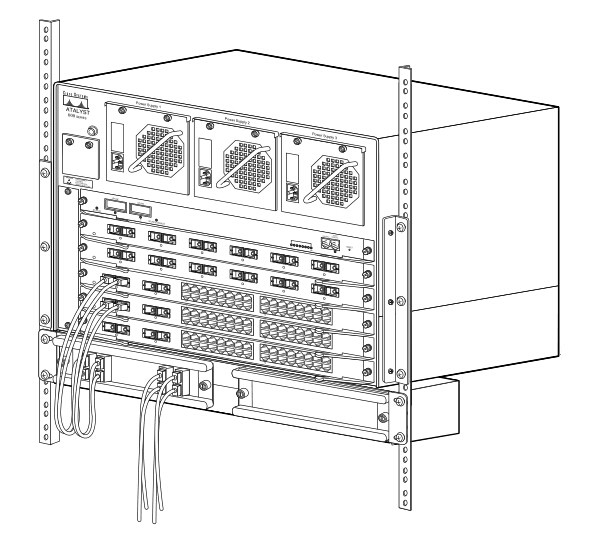
Connect Cables to a CWDM OADM
1. Insert the CWDM transceivers into the appropriate connectors on your switch if you have not already done so.
2. Insert the CWDM transceivers (color code/wavelength specific) into their respective switching module ports.
3. Clean all fiber optic connectors on the cabling before inserting them into the CWDM Mux/Demux connectors.
4.
Connect the single-mode fiber optic patch cable from the CWDM
transceiver (TX/RX) to the OADM module equipment connectors (TX/RX).
5. If you are using both channels of the CWDM OADM, then repeat step 4 for the second channel.
6.
Connect the west backbone single-mode fiber patch cable to the OADM
network west connector and connect the east backbone single-mode fiber
patch cable to the OADM network east connector.
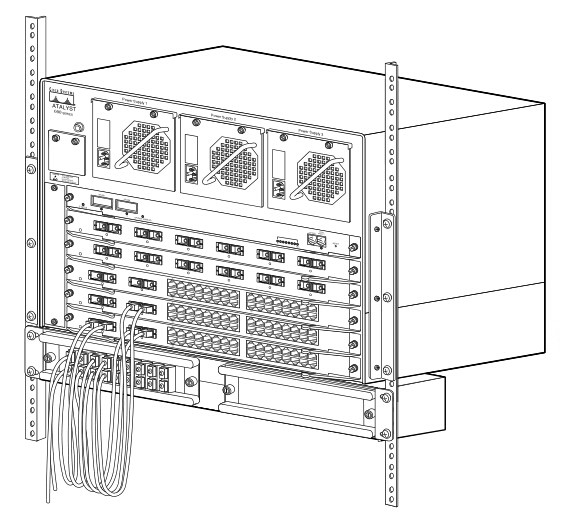
Connect Cables to a CWDM Mux/Demux (8-Channel)
1.Insert the CWDM transceivers (color code/wavelength specific) into their respective switches.
2.Clean all fiber optic connectors on the cabling before inserting into them into the 8-channel CWDM Mux/Demux connectors.
3.Connect
the single pair fiber optic cables from the CWDM transceivers (TX/RX;
up to eight channels) to the OADM module equipment connectors (TX/RX; up
to eight wavelengths).
4.Connect the backbone single pair fiber optic patch cables to the OADM network connector.
5.Connect the fiber optic patch cables from the CWDM transceivers (TX/RX) to the 8-channel Mux/Demux (TX/RX) connectors.
Summary
This
article provides installation instructions for the CWDM system, which
includes the system shelf installation, CWDM OADM and CWDM Mux/Demux
installation and removal, CWDM transceivers installation and removal as
well as connecting the CWDM OADM and CWDM Mux/Demux to the switch. The
optical components used in this process are as follows.
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/install-connect-cwdm-system.html
Originally published: www.fiberopticshare.com/install-connect-cwdm-system.html